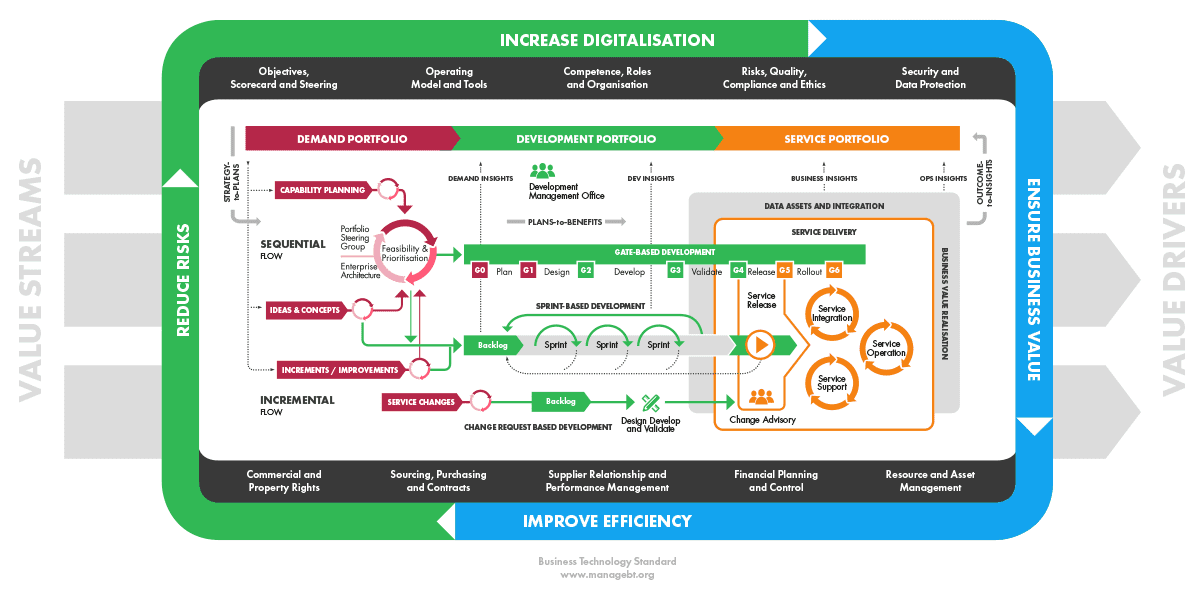
This chapter briefly describes the international technology management models and standards applied in the development of the Business Technology Standard.
ITIL, formerly known as Information Technology Infrastructure Library, is a set of guidelines and best practices for IT service management (ITSM). It is a registered trademark of AXELOS Limited. ITIL focuses on aligning IT services to the needs of businesses and supports its core processes. It is structured and published in five core volumes: service strategy, service design, service transition, service operation and continual service improvement.
The framework that ITIL provides can be adapted and applied to all business and organisational environments. It includes guidance for identifying, planning, delivering, and supporting IT services.
CMMI®, Capability Maturity Model Integration®, is an internationally reputed reference model providing guidance for improving processes to meet the business goals of an organisation. It is developed by industry experts, governments, and the Software Engineering Institute (SEI). The framework supports coordination of multi-disciplinary activities and systematic thinking.
COBIT 5, the Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology, is owned and supported by ISACA. The current version 5.0 consist of COBIT 4.1, VAL IT 2.0, and Risk IT frameworks.
COBIT 5 provides metrics and maturity models to measure whether or not the IT organisation has achieved its objectives. It also balances the needs of internal and external stakeholders.
PMBOK, the Project Management Body of Knowledge, is a set of standard terminology and guidelines based on internationally recognised project management methods provided by the Project Management Institute (PMI). PMBOK is a widely accepted and acknowledged standard and used as basis of many other project management methods.
PMBOK provides an in-depth description of the required content and fundamentals of a project but does not focus on giving hands-on implementation advice.
PRINCE2, Projects IN a Controlled Environment, is a de facto standard project management method owned by the UK Cabinet Office. PRINCE2 complements the PMBOK model by providing a process-based and practical guidance with ready-to-use templates for Project Managers and project steering groups in the different phases of a project. PRINCE2 ensures greater control of resources and effective management of business and project risks.
ISO/IEC 20000 is a service management system (SMS) and the first international standard for IT service management. It is owned by The International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). It is broadly aligned with ITIL.
The ISO/IEC 20000 has two parts. The first part defines the formal requirements for high-quality production of IT services to the business. It includes criteria for planning, service management, and service production as well as for customer / supplier management. The second part describes the processes of service production largely in the same way as the ITIL processes while focusing, however, more closely on customer/supplier management processes.
ISO 21500 is a standard that provides generic guidance on the concepts and projects of project management. It can be used by any type of organisation and applied to any type of project – irrespective of size, complexity or duration.
ISO 21500 is an informative standard rather than a certified methodology. It provides a high-level description of concepts and processes that are considered to form good practice in project management and places projects in the context of programmes and project portfolios. PMBOK is very much in line with ISO 21500 and vice versa.
ISO/IEC 38500 is a standard providing general principles for IT governance especially to managers with the highest level of business responsibility (such as board of directors and management team). It can be widely applied to all kinds of organisations of varying sizes, including public and private companies and non-profit organisations.
TOGAF the Open Group Architecture Framework, is an enterprise architecture framework that allows organisations to have a structured approach for governing the implementation of technology related especially to software technology design, development and maintenance. It was first published in 1995 and was based on the US Department of Defence Technical Architecture Framework for Information Management (TAFIM). It has been since developed by The Open Group Architecture Forum and released in regular intervals on the Open Group public website.
TOGAF aims at improving business efficiency by ensuring consistent methods, communication and efficient usage of resources. It ensures industry credibility with a common language among enterprise architecture professionals.
SAFe, Scaled Agile Framework is a framework and a set of best practices for enterprises for scaling agile development. The base of SAFe was developed in 2008 by Dean Leffingwell and is nowadays freely available by Scaled Agile, Inc.
SAFe has its emphasis on continuous improvement and managing workflows instead of single projects. It has gained influence from three main disciplines: agile software development, lean product development and systems thinking. The aim is to support alignment, collaboration and delivery across many agile teams.
DevOps, “Development” and “Operations”, is a methodology for software development. It has its basis in lean and agile approaches and consists of different methods, practices and tools or toolchains. By combining software development (Dev) and information technology operations (Ops), the aim is to shorten the systems development life-cycle, ensure high quality of productivity as well as provide fixes and updates that contribute to business objectives.
IT4IT is an open standard providing an IT framework for delivering value for business created by Open Group. It is vendor and technology-neutral reference architecture and operative model for leading business IT. IT4IT is based on value chain concept known as the IT Value Chain that has four value streams: strategy to portfolio, requirement to deploy, request to fulfil and detect to correct. The aim is to provide structure and tools for organising IT.
SIAM, Service Integration and Management, is an approach for managing multi-sourced service suppliers and integrating them to support a single business-facing IT organisation. SIAM is not a process, but rather a model for building service capability with a collection of best practices and tools. The aim is to provide better service to end-users via enhanced cost-efficiency, increased accountability and flexibility.